Earthquake Today: Understanding Our Dynamic Planet
Earth is constantly moving, with its tectonic plates shifting and interacting. This movement can cause sudden releases of energy, resulting in earthquakes. These events range from barely perceptible tremors to devastating megathrust quakes, shaping landscapes and impacting lives worldwide.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of earthquakes today, delving into the latest seismic activity around the globe. We’ll explore recent earthquakes, their locations, magnitudes, and potential impacts. Additionally, we’ll discuss resources for staying informed about earthquakes and essential safety measures to take in case of an event.
Recent Earthquake Activity (April 5th & 6th, 2024)

Here’s a glimpse into some of the earthquake today events as of April 6, 2024:
- East Coast Surprise: The United States East Coast experienced a significant earthquake on April 5. The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) measured the initial tremor at a magnitude of 4.8, with its epicenter near Lebanon, New Jersey. This event was considered the strongest in the Northeast in over a decade, and it caused shaking and rattled nerves across several states, including Maryland, Pennsylvania, and New Jersey. Later in the day, an aftershock of magnitude 4.0 followed.
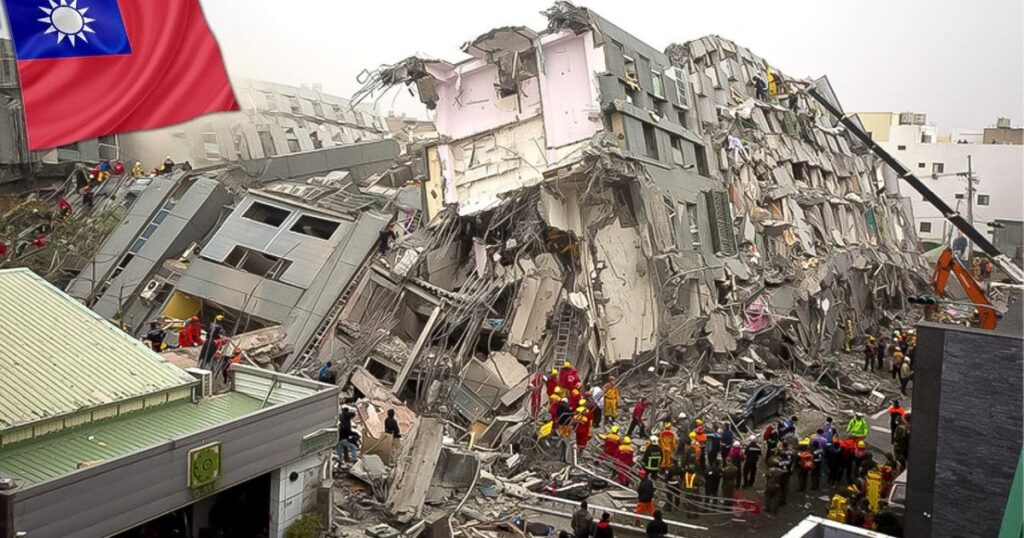
- Island Tremors: Taiwan witnessed a series of earthquakes on April 5, with magnitudes ranging from 4.6 to 4.9. These tremors were centered near Hualien City and are part of a frequently seismically active region.
- Global Seismic Activity: Several other earthquakes occurred globally on April 5th and 6th, including events in:
- Japan (Hokkaido and Honshu)
- Indonesia (North Sumatra)
- Solomon Islands (Makira)
- East Timor (Lautém)
- Peru (Oxapampa)
- El Salvador (Jujutla)
- Alaska (Kaktovik)
Staying Informed About Earthquakes:
Staying informed about events from the earthquake today is crucial for preparedness. Here are some valuable resources:
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS website provides real-time earthquake information, including maps, recent earthquake reports, and historical data: https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): NOAA’s National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) offers earthquake hazard information and resources https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/.
- European-Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC): This organization provides real-time and historical earthquake data for Europe and the Mediterranean region https://emsc-csem.org/.
- International Seismological Centre (ISC): The ISC compiles global earthquake data and offers searchable archives: https://www.isc.ac.uk/.
By following these resources, you can stay updated on earthquake today occurrences and potential aftershocks in your area.
Understanding Earthquake Magnitudes
The magnitude of an earthquake measures the energy released during the event. The Richter logarithmic scale is commonly used to quantify earthquake magnitudes. Each whole number increase on the Richter scale represents a tenfold increase in the ground motion’s amplitude.
Here’s a general breakdown of earthquake magnitudes and their potential impacts:
- Microtremors (Magnitude less than 2.0): Typically not felt by humans.
- Minor earthquakes (Magnitude 2.0 to 3.0): They may be felt as a slight vibration or tremor, but they rarely cause damage.
- Light earthquakes (Magnitude 3.0 to 4.0): Often felt but cause minimal damage to well-built structures.
- Moderate earthquakes (Magnitude 4.0 to 5.0) Can cause mild damage to poorly constructed buildings and may crack plaster in well-built structures.
- Strong earthquakes (Magnitude 5.0 to 6.0) Can cause significant damage to poorly constructed buildings and some cracks in well-built structures.
- Significant earthquakes (Magnitude 6.0 to 7.0) Can cause widespread damage, with some buildings collapsing.
- Great earthquakes (Magnitude 7.0 to 8.0) Cause severe damage over large areas, with many buildings collapsing.
- Mega-earthquakes (Magnitude more significant than 8.0): Devastating events that can trigger tsunamis and cause widespread destruction.

FAQs:
1: Is there a chance of an earthquake in Pakistan?
Pakistan is located on the boundary of two major tectonic plates, making it prone to earthquakes. While earthquake occurrences today cannot be precisely predicted, historical records and geological settings suggest the possibility of future events.
2: Where is the biggest earthquake today (as of April 6, 2024)?
Based on available information, the strongest earthquake today appears to be centered near Lebanon, New Jersey, in the United States, with a magnitude of 4.8.
3: When was the last earthquake in Pakistan in 2024?
Unfortunately, real-time earthquake data isn’t readily available for this response. Still, some resources, like the USGS or Pakistan Meteorological Department, can be checked for the most recent tremors at https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/map/ and https://seismic.pmd.gov.pk/.
4: How big is a 4.8 earthquake?
A 4.8 magnitude earthquake falls under the “light earthquakes” category on the Richter scale. These events are often felt but cause minimal damage to well-built structures.
5: Is a 10.0 earthquake real?
Earthquakes with a magnitude of 10.0 are not theoretically impossible, but they are scarce. The Richter scale is logarithmic, so a 10.0 earthquake would release significantly more energy than a 9.0 earthquake.
6: What is a 10.0 earthquake?
Since a 10.0 earthquake hasn’t been recorded, its exact effects are hypothetical. However, scientists believe it would cause catastrophic damage on a global scale, trigger massive tsunamis, and potentially alter the planet’s rotation.
7: Is a 9.5 earthquake big?
Yes, a 9.5 earthquake is a massive event. The largest earthquake ever recorded was a 9.5 magnitude quake in Chile in 1960. Such earthquakes can cause widespread devastation, including collapsed buildings, tsunamis, and landslides.
8: What’s the worst earthquake size?
The “worst” earthquake size depends on the context. However, from a purely destructive standpoint, earthquakes exceeding 9.0 magnitude are considered the most catastrophic.
9: What is the strongest earthquake ever recorded?
The strongest earthquake ever recorded was a 9.5 magnitude event in Valdivia, Chile, on May 22, 1960.
10: What is a lousy earthquake?
The severity of an earthquake’s impact determines whether it’s considered “bad.” Magnitude, location, population density, and building construction quality all play a role. Generally, earthquakes above magnitude 6.0 can cause significant damage and casualties.
11: What size is a strong earthquake?
On the Richter scale, earthquakes between 5.0 and 6.0 magnitude are classified as “strong.” These events can cause significant damage to poorly constructed buildings and cracks in well-built structures.
12: How strong is a strong earthquake?
Strong earthquakes (magnitude 5.0 to 6.0) can cause noticeable shaking and potential injuries. While they may not cause widespread destruction, they can be frightening and disrupt infrastructure.





